Talent mapping starts with a simple idea: organizations grow when they view people as developing talents, not just resumes, and connect these abilities to future goals.
Every successful hire or promotion relies on a plan that helps leaders move from uncertainty to confident decisions. Talent mapping helps HR and TA Managers organize scattered profiles from ATS or HRM systems into a clear view of skills, readiness, and market options. This guide covers what talent mapping is, how to build a competency matrix, and when organizations in Vietnam should decide to build or buy talent before hiring becomes costly or slow.
TL;DR
- Talent mapping aligns skills, potential, and market availability with business strategy, enabling predictable and higher-quality hiring outcomes.
- Framework: A robust mapping process follows four phases: defining competencies, detailing skill descriptors, analyzing job requirements, and identifying talent gaps.
- Vietnam Context: In Vietnam, understanding passive candidate behaviors and the expanding tech landscape is critical for building resilient talent pipelines.
- Outcome: Predictable pipelines, better succession planning, and a measurable competitive edge in high-demand sectors
What is talent mapping?
Talent mapping is the strategic process of identifying, analyzing, and organizing information about current employees and external candidate pools to anticipate future workforce needs. Rather than reacting to vacancies, businesses use talent maps to tell the story of “who we will need next” and “how close we already are.” It connects individual strengths to organizational direction, workforce planning, and blending care for people with the disciplined vision of leadership.
Read more: Strategic Workforce and Talent Planning: Guidelines for business needs

Talent Mapping vs Candidate Mapping: Key Differences
Candidate mapping focuses solely on outside candidates for expedited hiring, whereas talent mapping encompasses both current employees and the broader market. Candidate mapping asks, “Whom can we hire this quarter?” Talent mapping asks, “What will our organization look like in three years?” The primary difference lies in the long-term focus and who is responsible talent mapping is a leadership tool, not merely a recruiting task.
5 Benefits of Talent Mapping for HR Planning
Enhanced recruitment efficiency
Talent mapping makes hiring more efficient by building pools of qualified candidates before jobs open up. Recruiters spend less time searching for unknown people and more time talking to the right professionals. This approach moves from cold outreach to informed conversations, saving time on unsuitable applicants.
Greater return on hiring investment
A mapped process protects hiring budgets. By assessing competencies objectively, businesses avoid expensive mis-hires and repeated onboarding cycles. Quality of hire becomes measurable, delivering stronger ROI than speed metrics alone.
Improved workforce planning
Workforce planning is most effective when leaders understand their team’s true capabilities. Talent maps provide options for succession planning, key roles, and future hiring needs. This supports the main article “Strategic Workforce & Talent Planning: Guidelines for today’s business needs.” Talent mapping provides the data that drives smart planning and supports future approaches in modern organizations.
Better learning and development strategies
Mapping shows which skills can be developed within the company. Learning and development teams can then create programs based on real data, not guesses. Employees also see clear career paths that match their skills.
Competitive edge in talent acquisition
Organizations that use the talent maps approach the job market with confidence. They know where hard-to-find candidates are and what motivates them. This advantage is especially important in the tech industry, where needs change rapidly.
4 Steps to Build Talent Mapping
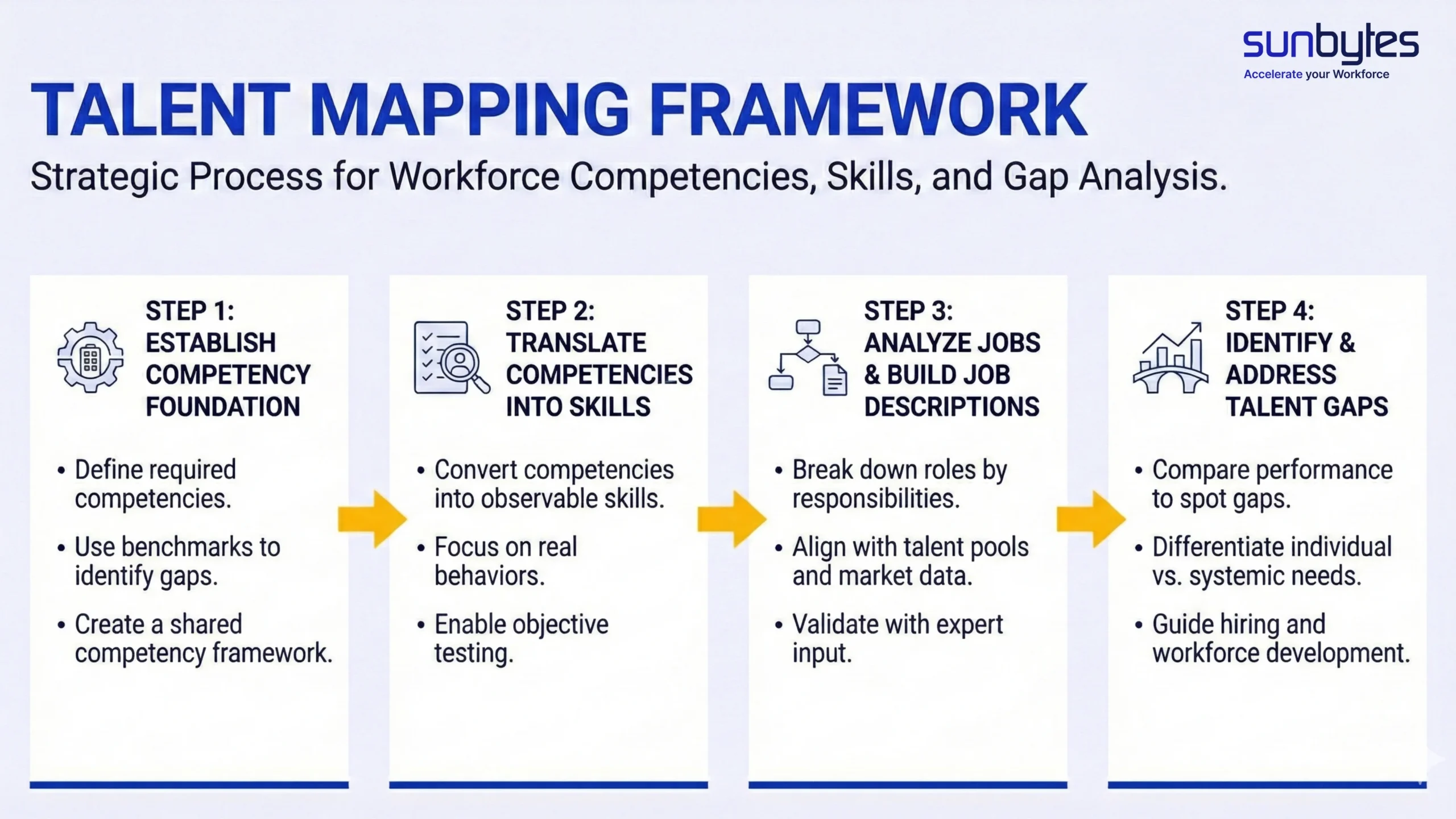
Step 1 – Establish groundwork for competencies
Organizations need to know what talents employees need to meet their goals, such as knowledge, skills, and other qualities. Tools like ATS, HRM, or CRM can help identify these needs. Comparing your internal standards with industry benchmarks can also help you spot any gaps.
Setting up competencies creates a common language and clear levels of seniority. This keeps mapping fair and objective. Leaders at all levels should review and approve this foundation. It’s like preparing the ground before building your talent pipeline.
Read more: Developing Talent Pipeline for High-Impact Roles in Evolving Industries
Step 2 – Describe skills for objective assessments
Next, teams turn competencies into clear, observable skills. These descriptions should help with tests, interviews, and career growth. Avoid using job titles without explaining the specific behaviors they represent. In Vietnam, showing real skills is more important than a long CV. Clear skill descriptions help avoid bias and let recruiters explain roles confidently.
H3: Step 3 – Analyze jobs & develop job descriptions
Mapping needs a clear understanding of each job. Teams break down responsibilities, technology used, and business goals. Job descriptions connect talent pools to actual hiring. Without this step, talent maps are just theory.
Examine data from similar roles in other departments. Compare salary ranges and expectations when considering a role change. For senior jobs, get advice from executive search experts.
Read more: Executive Search and Recruitment: 6 Key Differences and 7 Advantages Explained
Step 4 – Identify gaps in your talent mapping framework
Organizations carefully compare the real skills shown at work with employees’ self-assessments to find any gaps. These gaps often show up with junior staff or new hires who need clear growth plans. Experienced professionals can mentor them, sharing knowledge and building their confidence.
Some gaps come from changes in the market, global events, or new technology standards. These issues usually affect many people, so the whole organization needs to learn new skills together. Spotting these gaps early helps leaders understand the talent market and manage expectations calmly.
Finding these gaps turns talent mapping into a management tool. It helps leaders balance new opportunities with discipline, making sure hiring, succession, and training meet real needs, not just guesses.
Talent Mapping in Vietnam Context for Foreign Employers
Vietnam tech & professional talent landscape
Vietnam is transitioning from a production-focused economy to one that prioritizes skills and talent, with emerging communities in technology and high-value professional services. What once attracted businesses mainly through cost advantage now draws attention through scalability, domain expertise, and long-term workforce resilience. For HR and TA managers, mapping talent in Vietnam offers a clearer view of where critical skills are concentrated before recruitment plans are finalized.
Rather than entering the market with assumptions shaped in other countries, organizations that study Vietnam pools early are better prepared to administer salary expectations, seniority levels, and career mobility. Talent mapping therefore becomes a bridge between regional growth ambitions and localized people strategy.
Passive candidate behaviors in Vietnam
Senior candidates in Vietnam are largely passive and relationship-oriented; they respond to trustful conversations more than to job advertisements. Recruiters who approach without competency evidence often meet silence or short-lived engagement. HR managers also notice that architecture alignment and practical skill proof weigh heavily in decision making.
A respectful outreach style — explaining tests, growth paths, and organizational purpose will protects the employer brand from what many TA teams call “404 expectations.” Understanding these behaviors helps TA managers design engagement stages that feel relevant instead of intrusive
Talent Mapping Examples

Talent maps are visual tools that show key employee data. They often appear as matrices or tables. These maps highlight information like skill sets, job roles, and how ready staff are for new positions. They match roles with the skills needed and the people who have or are building those skills.
Once you have the necessary data, making the matrix is simple. Begin by listing the primary roles within your department. Then, identify the key skills for each job. Finally, assess how well-prepared your employees are for these roles by evaluating their current skills and growth potential. Here are basic examples of talent mapping in action:
Example 1: Tech head talent map
In this example, the talent map provides an easy-to-digest look at the essential skills required for two key positions and the readiness of potential candidates. The readiness levels indicate the estimated time it would take to fully prepare each individual for the role, based on their current skills and career growth path. Here, the matrix can help guide succession planning decisions and identify areas requiring workforce development.
| JOB ROLE | SKILL | INDIVIDUAL READINESS | ||
| 0-2 years | 2-3 years | 3+ years | ||
| IT Manager | Business Analysis IT Project Implementation | Person A | Person B,C | |
| Data Analysis | Analytics architecture Data engineering governance | – | Person D | Person E |
The matrix shows two IT Manager successors ready within two years, yet a pipeline gap follows. No internal candidate can assume the Data Analysis Lead role in the near term, signaling the need for external sourcing or accelerated upskilling.
Example 2: Senior Full-Stack Engineer
Talent mapping for Senior Full-Stack Engineers helps companies balance technical progress with quality control. In our Flexpress project, this method shifted hiring from urgent searches to a more organized approach. HR leaders could choose candidates based on system fit, automation plans, and readiness for busy operations. By working with Sunbytes, Flexpress expanded from a single offshore engineer to a full experts team in Vietnam and the Netherlands, handling migration, DevOps, and email marketing for over 50 million users. This example demonstrates how a robust talent map and a dependable IT partner dedicated to recruitment help TA managers scale up, deliver results faster, and enhance hiring outcomes at every stage.
See full Flexpress story here: Scaling Projects with Human Expertise
Measurable Metrics for Talent Mapping Effectiveness

Measuring outcomes ensures that talent maps remain credible in the eyes of management and useful for daily TA operations. HR and TA managers should observe:
Time to productivity – how quickly mapped hires contribute to objectives
Quality of hire – performance and retention after onboarding
Talent pipeline ratio – readiness of pools versus requisition volume
Learning readiness index – degree of gap closure through development
Metrics transform talent mapping into a governance dashboard that aids HR managers in grasping what is unfolding in the market these days and offers opportunities to discipline management expectations.
5 tips for optimizing talent mapping
Use comprehensive data
Talent mapping should use both internal ATS/HRM data and outside information, along with objective tests. Just using tools may reassure recruiters, but HR managers want reliable results. The more data you have, the more flexible you can be when explaining pipelines to hiring leaders.
Match transferable skills to career paths
Talent maps are most useful when they show how skills can move across different roles and levels. This helps employees see their growth options and lets TA managers suggest other talent pools before hiring gets costly or slow.
Consider skills tests
Objective assessments protect engagement from bias and inflated CV claims. In Vietnam, practical proof builds trust for both HR and TA managers. Tests should be introduced as growth gates rather than barriers so candidates understand the organizational purpose behind them.
Gather continuous feedback from stakeholders
A talent map is a living conversation among departments. Feedback ensures that promise and delivery stay aligned. HR managers appreciate this listening rhythm because it safeguards service quality and succession discipline.
Evaluate current talent processes, systems, and resources
A talent map is only as good as the processes that support it. Check each step, from finding talent pools to mentoring and promotions, to spot any unclear or slow parts. Ensure your HR technology provides accurate and easy-to-understand insights. If not, focus on better data integration and analytics. Finally, build up your TA and HR team’s skills with training or expert advice so your organization can confidently manage talent pipelines.
Focus areas:
- streamline manual work with automation
- connect data across ATS × HRM × assessments
- expand reporting for talent ROI & readiness
- train teams on engagement and skills tests
About Sunbytes
Sunbytes is a Dutch technology company based in the Netherlands, with a delivery hub in Vietnam. For 14 years, we have helped international teams accelerate their workforce quickly and sustainably through recruitment and workforce support.
What sets Sunbytes apart is that our Accelerate Workforce Solutions is grounded in real delivery expertise. Through end-to-end Digital Transformation Solutions covering custom software development, QA/testing, and long-term product support, we deeply understand how high-performing product and engineering teams are built and operated. This delivery-first perspective enables clearer role definitions, stronger candidate matching, and faster onboarding. In addition, our Secure by Design cybersecurity mindset ensures that teams scale with consistent standards, stronger risk awareness, and compliance readiness as organizations grow across borders.
With Sunbytes, you do more than add headcount. You build a team that is ready to deliver, integrates smoothly, and grows with your roadmap.
Talent Mapping at Sunbytes
At Sunbytes, we utilize talent mapping as a strategic approach to aligning workforce skills with long-term business objectives, rather than just addressing immediate hiring needs. We support organizations in keeping their Vietnam-based and cross-border talent pools accurate and well-managed, so HR Managers and Talent Acquisition leaders can plan ahead and make confident decisions instead of reacting to last-minute needs.
Our approach to talent mapping focuses on skills and works across borders, making it easier to align teams and scale up as a real extension of your business. We connect with top passive candidates in technology and professional services, helping you hire faster, use your budget wisely, and get better results from your hiring efforts.
Reach out to see how Sunbytes can help you build, secure, and operate resilient talent pipelines with confidence.
FAQs
Effectiveness is evaluated through quality, not just speed: performance of hires, succession readiness, and how accurately the map predicted real vacancies.
Senior pools should be updated quarterly in Vietnam tech sectors and bi-annually for stable functions.
Gap identification compares competency framework, assessments, and job outcomes to decide build/buy strategy, directly feeding workforce planning and L&D design.
Let’s start with Sunbytes
Let us know your requirements for the team and we will contact you right away.


