In today’s digitally driven economy, robust cybersecurity compliance is indispensable for safeguarding business operations, preserving customer trust, and maintaining competitive advantage. European regulations surrounding cybersecurity have multiplied, creating benchmarks businesses must proactively integrate into their strategies.
In this article, we will simplify Europe’s top 10 cybersecurity laws, clearly outlining their activation dates, compliance deadlines, and required security assessments. This will empower your business to approach these compliances confidently.
Key Cybersecurity Compliance Regulations in Europe
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Safeguarding Personal Data Privacy
The GDPR, enacted on 25 May 2018, enforces rigorous privacy standards for any entity handling EU residents’ data across healthcare, fintech, e-commerce, and technology sectors. Noticeably, key provisions include Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), consent management, and obligatory breach notifications within 72 hours.
Here are the most common entry points for errors:
- Activation Date: May 25, 2018
- Compliance Requirements: DPIA, explicit consent management, breach mandatory notification to the authorities.
- Security Assessment: Implicitly required
- Penalties: Up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher.

NIS2 Directive: Protecting Critical Infrastructure
The NIS2 Directive, effective since January 16, 2023, targets enhanced cybersecurity resilience for essential services and digital infrastructures, including energy, transport, healthcare, financial services, and digital service providers. Also, it’s mandatory for the supply chain. If you’re delivering services to a company within the NIS2 scope, you’ll need to show you’re NIS2 compliant just as well, while not falling within the scope yourself.
- Activation Date: January 16, 2023
- Compliance Deadline: October 17, 2024
- Assessment: Mandatory risk assessment and cybersecurity training validation
- Non-compliance: Up to €10 million or the possibility of 2% of the worldwide annual turnover

Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA): Fortifying Financial Cybersecurity
Focused exclusively on the finance sector (banks, fintech, insurance companies), DORA (activated January 16, 2023) standardizes operational resilience through mandatory penetration testing, security audits, robust incident management frameworks, and supply chain compliance.
- Activation Date: January 16, 2023
- Compliance Deadline: Local deadlines apply
- Assessment: Mandatory penetration testing, resilience audits every three years minimum.
- Penalties: up to 2% of a firm’s total annual worldwide turnover, while individuals face a maximum fine of €1 million.

Digital Services Act (DSA): Promoting Safer Digital Experiences
The Digital Services Act (DSA), enacted on November 16, 2022, targets platforms like e-commerce websites and social media networks. Compliance involves rigorous content moderation practices and increased transparency measures to ensure user protection.
- Activation Date: November 16, 2022
- Compliance Deadline: February 17, 2024
- Assessment: Implementation validation required
- Non-compliance:
6% of annual worldwide turnover: This is the maximum fine that can be imposed for failure to comply with DSA obligations.
1% of annual worldwide turnover: This applies to providing incorrect, incomplete, or misleading information, failing to reply or rectify such information, or failing to submit to an inspection.
5% of the average daily worldwide turnover: This applies to delays in complying with a decision or request of the Digital Services Coordinator, or for obstructing or hindering the commencement or conduct of an inspection.

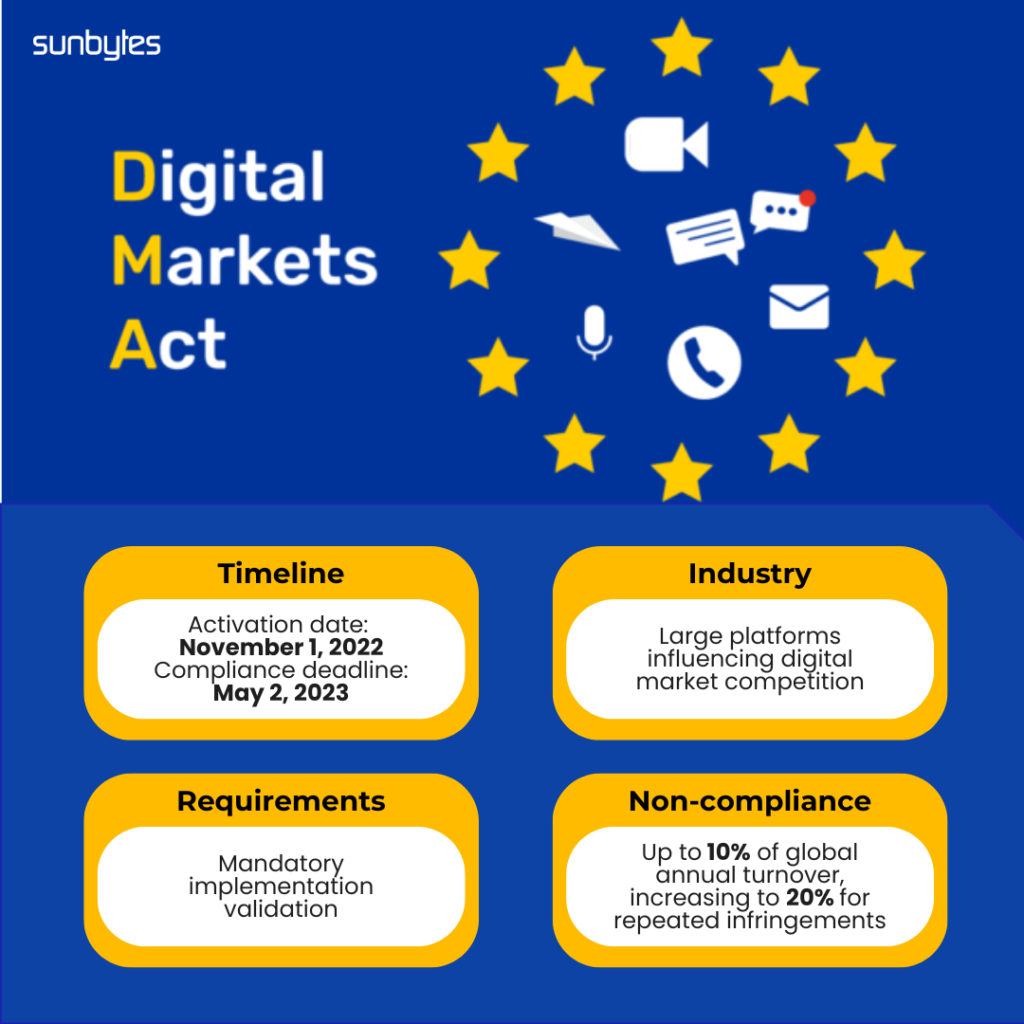
Digital Markets Act (DMA): Ensuring Fair Digital Competition
Activated November 1, 2022, DMA regulates “digital gatekeepers” – large platforms influencing digital market competition. Compliance obligations mandate platform transparency and fair competitive practices.
- Activation Date: November 1, 2022
- Compliance Deadline: May 2, 2023
- Assessment: Mandatory implementation validation
- Penalties: Up to 10% of their global annual turnover, increasing to 20% for repeated infringements, with the European Commission also able to impose periodic penalty payments.
Data Governance Act (DGA): Safe and Ethical Data Sharing
Effective since June 23, 2022, the Data Governance Act facilitates secure data sharing primarily within healthcare, technology, and data intermediaries, ensuring transparency and security in data handling and exchange.
- Activation Date: June 23, 2022
- Compliance Deadline: September 24, 2023
- Assessment: Implementation validation required
- Consequences: This doesn’t specify penalties itself; instead, it delegates the responsibility for establishing penalties to each member state, ensuring they are effective, proportionate, and dissuasive.

Cyber Resilience Act (CRA): Securing Digital Products
Scheduled activation on October 23, 2024, CRA covers a broad range of hardware and software products with digital elements that can connect to a network, aiming to enhance their cybersecurity throughout their lifecycle, with specific exclusions for sectors like medical devices and products for national security.
- Activation Date: October 23, 2024
- Compliance Deadline: December 11, 2027
- Assessment: Third-party penetration testing required
- Fines: up to €15 million or 2.5% of a company’s global annual turnover for breaches of core cybersecurity requirements

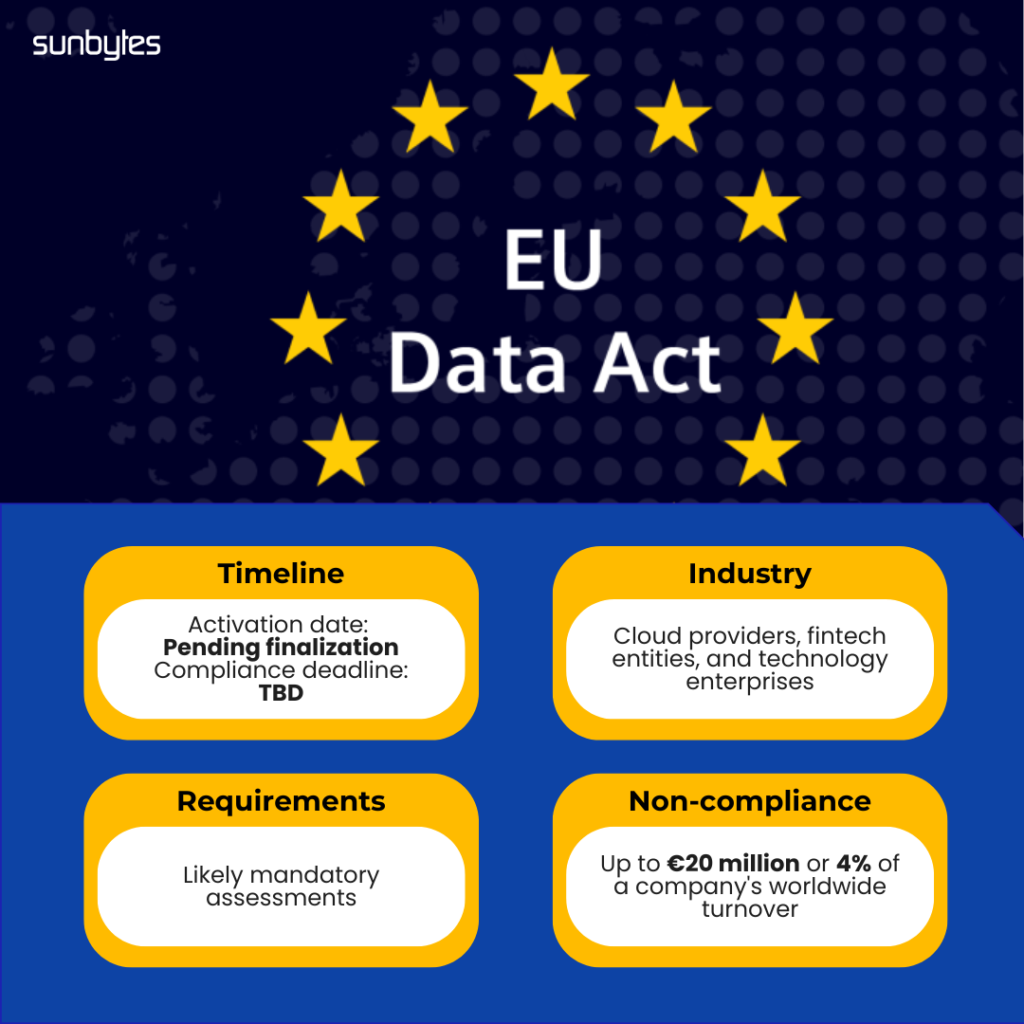
Data Act: Empowering Data Transparency and Portability
Currently drafted, the Data Act aims to empower individuals and businesses through enhanced data portability and increased transparency, directly impacting cloud providers, fintech entities, and technology enterprises.
- Activation Date: Pending finalization
- Compliance Deadline: TBD
- Assessment: Likely mandatory assessments
- Fines: up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s worldwide turnover, whichever is higher.
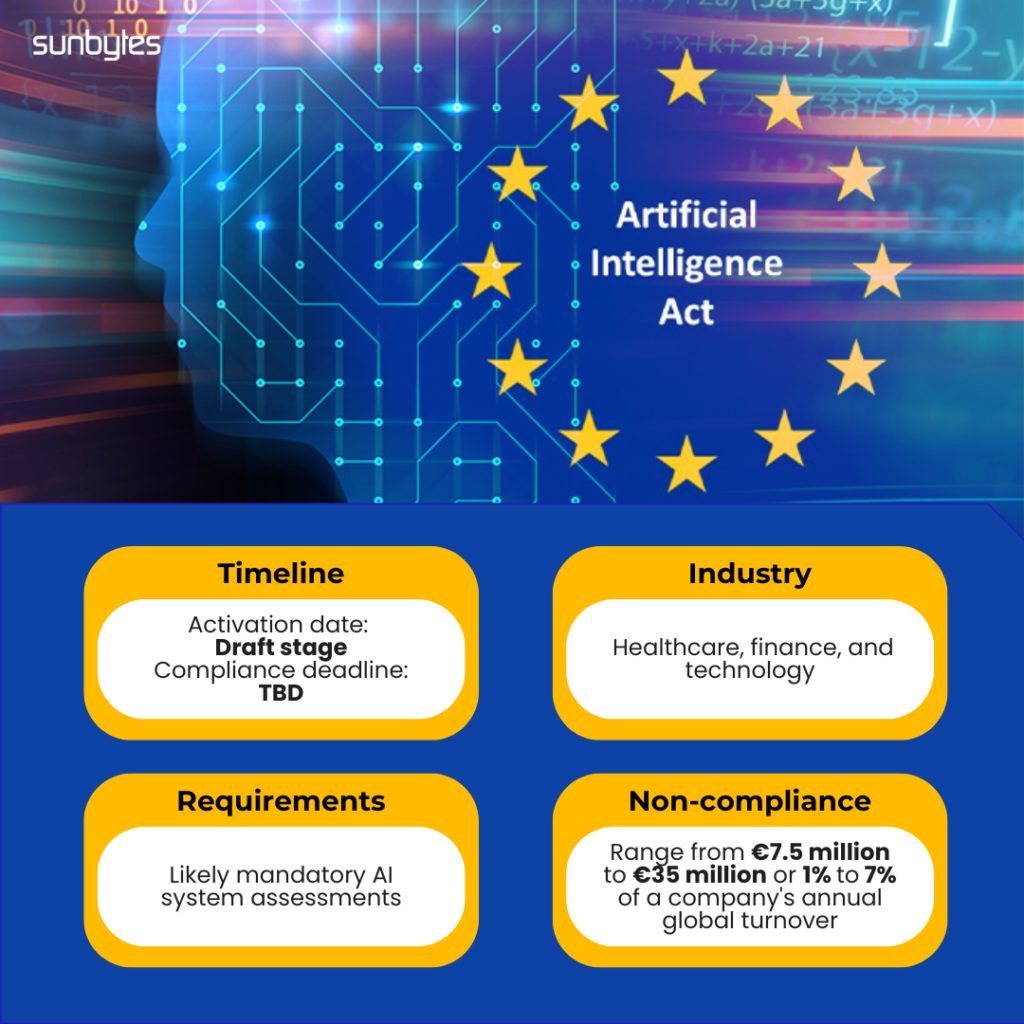
Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act): Governing Ethical AI Development
Another draft regulation, the AI Act, intends to standardize ethical AI usage across industries, including healthcare, finance, and technology. It introduces systematic AI risk management procedures to mitigate potential misuse.
- Activation Date: Draft stage
- Compliance Deadline: TBD
- Assessment: Likely mandatory AI system assessments
- Non-compliance: fines can range from €7.5 million to €35 million or 1% to 7% of a company’s annual global turnover, depending on the severity of the infringement.
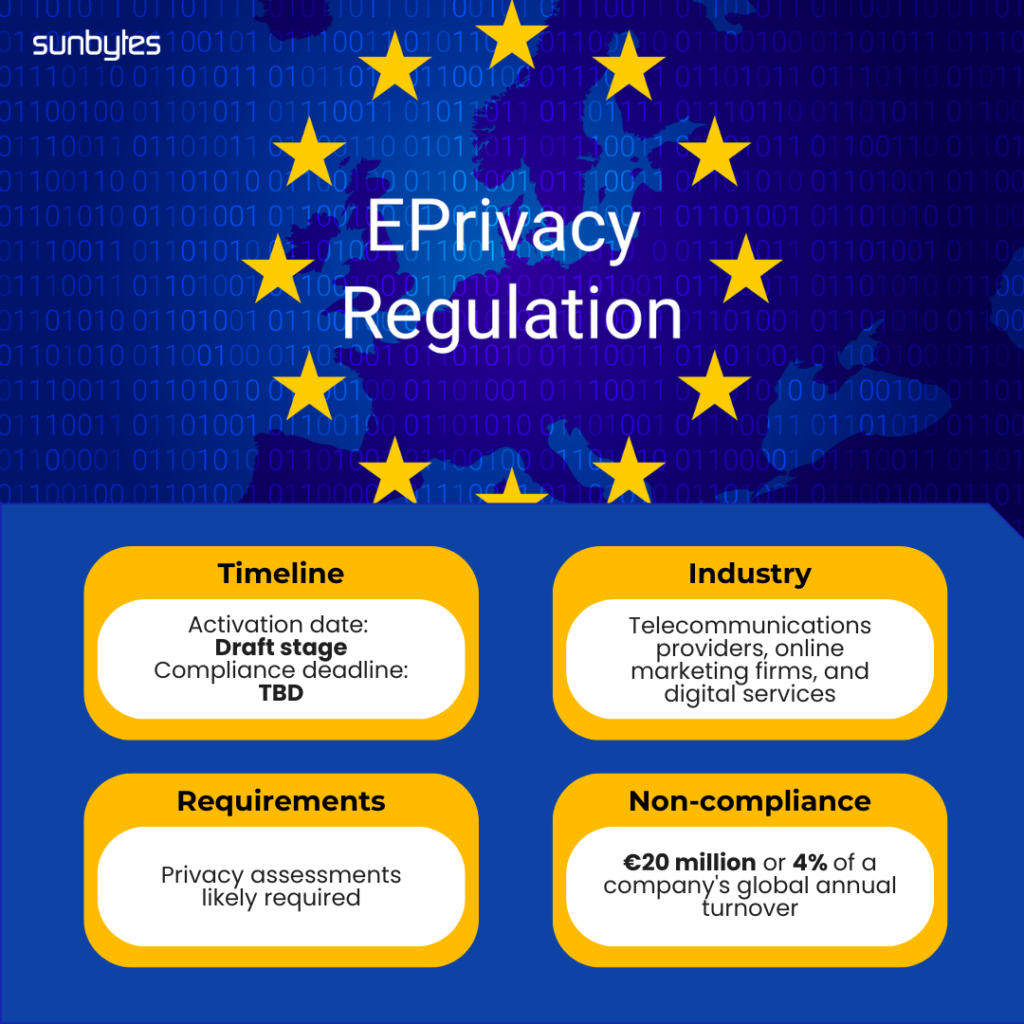
ePrivacy Regulation: Strengthening Digital Communications Privacy
The draft ePrivacy Regulation is designed to augment digital communications privacy protection, affecting telecommunications providers, online marketing firms, and digital services.
- Activation Date: Draft stage
- Compliance Deadline: TBD
- Assessment: Privacy assessments are likely required
- Fines: potential penalties of up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
Proactively Meeting Compliance Through Cybersecurity Assessments
To actively meet EU Cybersecurity Compliance requirements, companies must execute a structured cybersecurity assessment strategy:
Conduct Comprehensive Risk Assessments
Conduct systematic assessments annually or biannually to promptly identify security gaps and vulnerabilities within business processes. Tailor methodologies specific to your industry for enhanced accuracy and relevance.
Penetration Testing as a Compliance Benchmark
A penetration test replicates cyberattacks under controlled conditions, proactively identifying security weaknesses. Essential stages include:
- Scoping the testing environment
- Performing rigorous security testing
- Comprehensive reporting and actionable feedback
For robust security hygiene, penetration tests should occur at least annually, preferably through certified external experts for unbiased, accurate assessments.
Read our complete guide to penetration testing to know how it helps your business stay compliant.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
Under GDPR, DPIAs systematically identify and minimize data privacy risks in processing activities involving personal data. Avoid common DPIA pitfalls by conducting them methodically and integrating them seamlessly within your compliance framework.
Secure Your EU Compliance With Our Penetration Testing Services
Penetration testing has rapidly become integral to compliance strategies, significantly mitigating risk exposure and ensuring regulatory readiness. With extensive experience, specialized industry knowledge, and a personalized approach, our penetration testing services directly address your unique cybersecurity challenges.
Secure your organization’s compliance today – schedule a penetration testing consultation and confidently navigate Europe’s cybersecurity regulations.
Let’s start with Sunbytes
Let us know your requirements for the team and we will contact you right away.


